Architecture¶
The airshipctl tool is designed to work against declarative infrastructure
housed in source control and manage the lifecycle of a site.
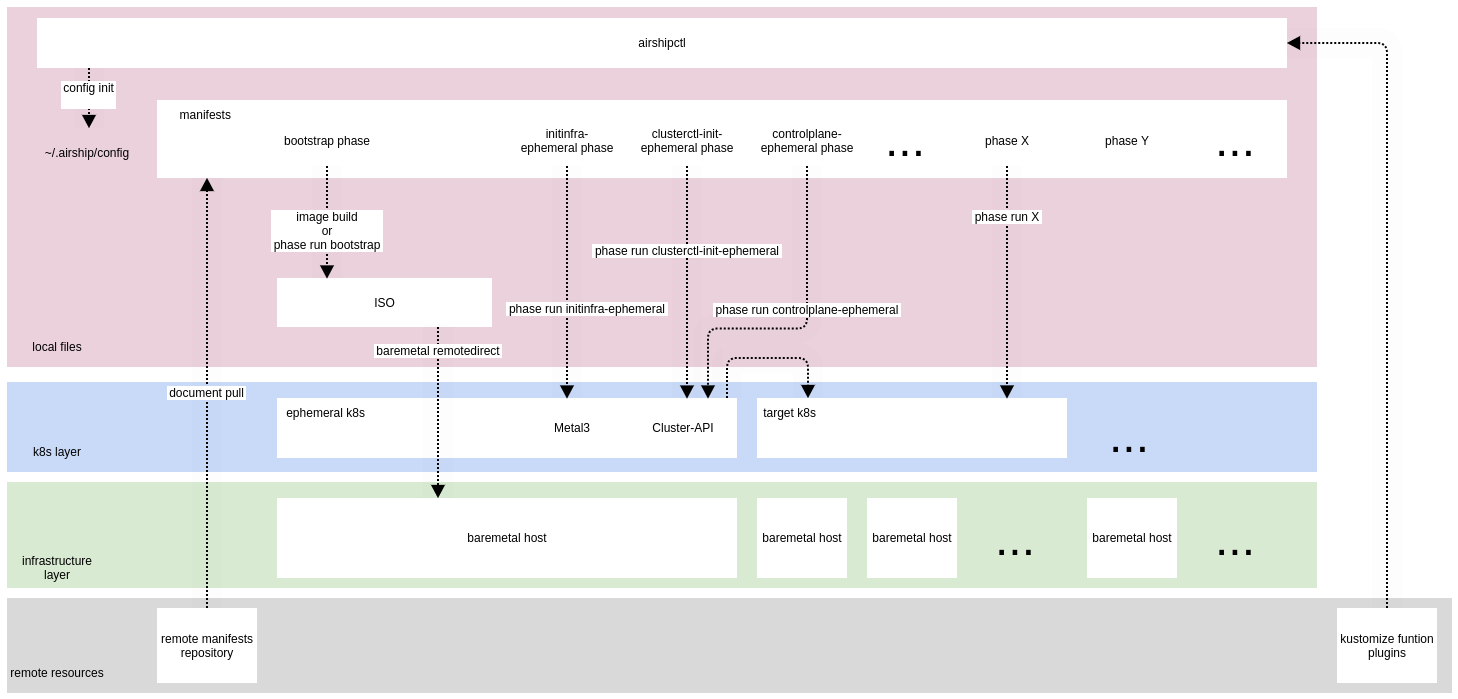
Example Usage¶
In a nutshell, users of airshipctl are able to do the following:
Create an
airshipctlconfiguration file.airshipctlcan create a default configuration file (~/.airship/config) running the commandairshipctl config init. Users can modify the config file according to their needs.Run
airshipctl document pullto clone the document repositories defined in theairshipctlconfig file. These repositories contain declarative documents which are used to bootstrap and manage infrastructure, kubernetes clusters and workloads.When deploying against baremetal infrastructure, run
airshipctl image buildto generate a self-contained ISO that can be used to bootstrap an ephemeral Kubernetes node on top of a baremetal host.NOTE: Most of the
airshipctlfunctionality is implemented as phases. Whenairshipctlperforms an action, it likely runs a phase or multiple phases defined in phase documents.airshipctl phasecommand can be used to run a specific phase. For example to build the ISO one can run the commandairshipctl phase run bootstrapOnce the ISO is generated, run
airshipctl baremetal remotedirectto remotely provision the ephemeral baremetal node and deploy a Kubernetes instance thatairshipctlcan communicate with for subsequent steps. This ephemeral host provides a foothold in the target environment so we can follow the standard cluster-api bootstrap flow.Run
airshipctl phase run initinfra-ephemeralto bootstrap the new ephemeral cluster with the necessary infrastructure components to provision the target cluster.Run
airshipctl phase run clusterctl-init-ephemeralto install cluster-api components to the ephemeral Kubernetes instance.Run
airshipctl phase run controlplane-ephemeralto create cluster-api objects for the first target cluster which will be deployed using cluster-api.
Further steps depend on what exactly a user wants to have as a result. Usually, users transform their first target cluster into a cluster-api management cluster and then use it to deploy workload clusters. To transform a Kubernetes cluster into a cluster-api management cluster, it is necessary to deploy infrastructure components and the cluster-api components.
As users evolve their sites declaration, whether adding additional
infrastructure, or software declarations, they can create phase definitions to apply those
changes to the site using builtin phase executors and run those phases using the command
airshipctl phase run <phasename>.